Project Timeline: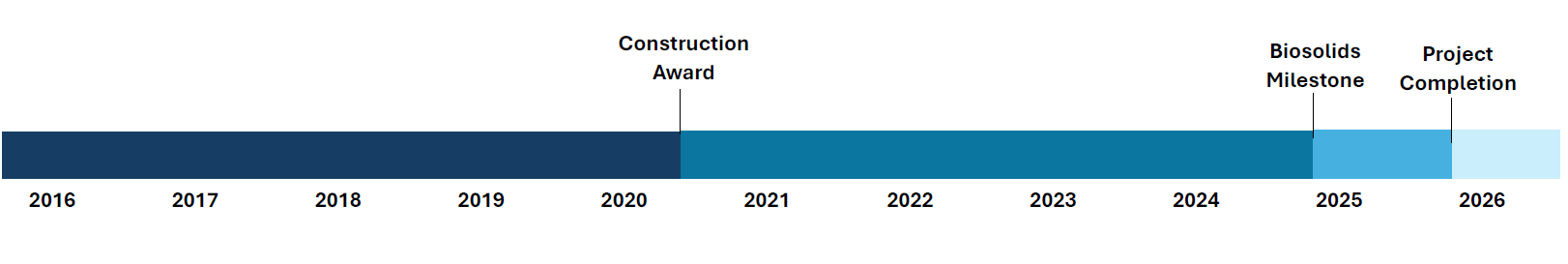
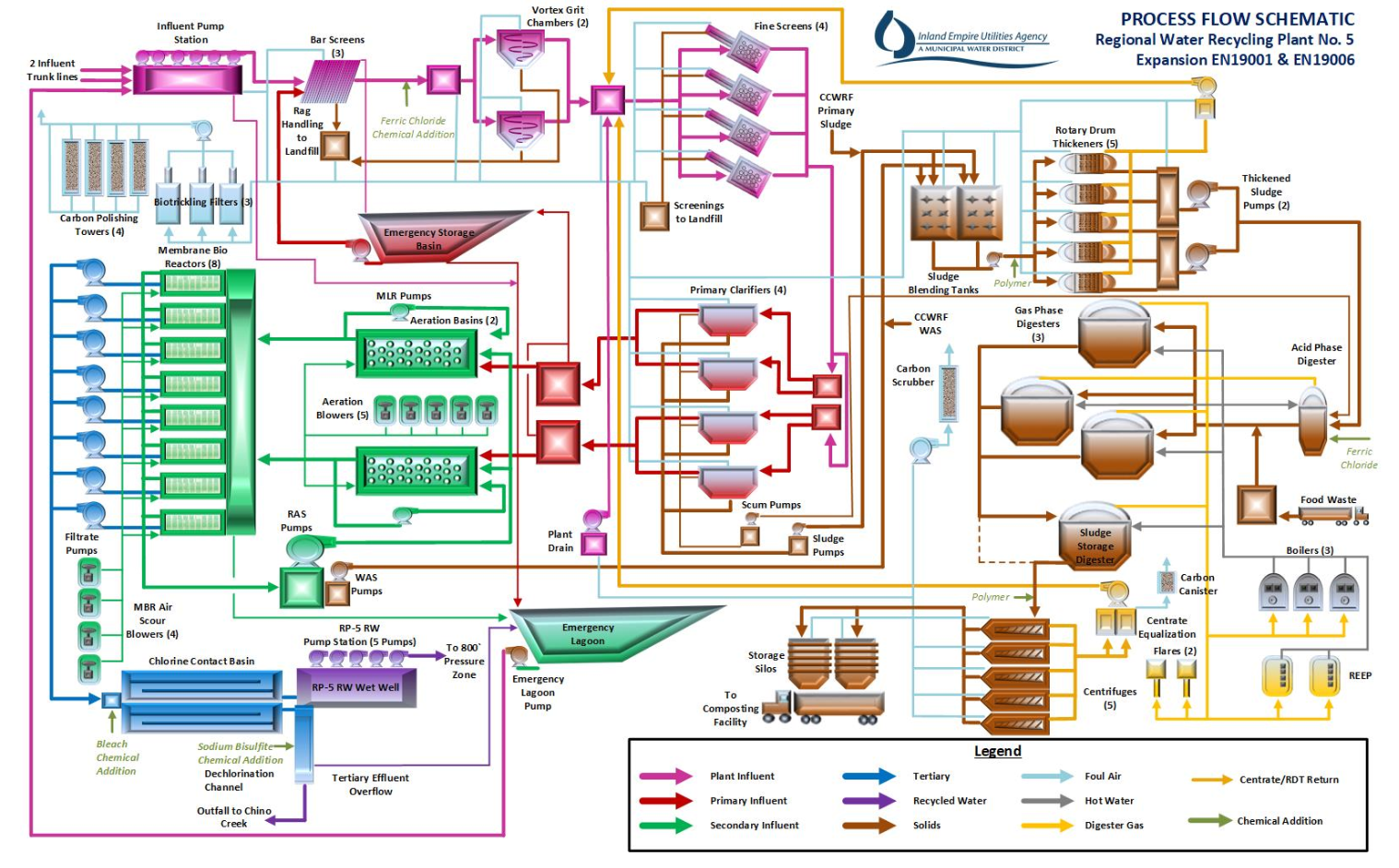
Regional Water Recycling Plant No. 5 (RP-5) has been in operation since 2004, currently treats liquids only, and has a capacity of 16.3 million gallons per day (mgd). Water treated from RP-5 is either discharged to Chino Creek, delivered to industrial users, or pumped to basins for groundwater recharge. Of the five plants, RP-5 is located at the lowest elevation and is an end-of-the-line wastewater treatment plant, making it the receiver for any flows that the other plants cannot handle. RP-5 Liquids Treatment Expansion project will expand RP-5’s liquid treatment capacity to 22.5 mgd. The project will include infrastructure for RP-5’s ultimate buildout to treat an average flow of 30 mgd and a peak flow of 60 mgd.
Regional Water Recycling Plant No. 2 (RP-2) has been in operation since 1960 and operated liquids and solids treatment sections until RP-5 was constructed to handle the liquids treatment section portion of RP-2. Solids are removed from Carbon Canyon Water Recycling Facility (CCWRF) and RP-5 and treated at RP-2. The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers will raise the spillway height of nearby Prado Dam and as a result RP-2 will fall within the dam’s floodplain. Before completion of the spillway project, a new solids treatment facility will be constructed and in operation at RP-5 to allow the decommissioning of RP-2.
The RP-5 Liquids Treatment Expansion and the RP-5 Solids Treatment Facility will be constructed under the one construction contract with two separate milestones. The milestones will be established to differentiate the time necessary to complete the solid treatment work necessary to facilitate the decommissioning of RP-2.
The plant will meet all regulatory requirements, utilize energy efficient equipment, and continue to provide recycled water to the service area as it continues to grow.
Construction Cost & Funding:
- Construction Cost: $330 million
- Low interest rate loans.
- $196 million loan from the EPA Water Infrastructure Finance and Innovation Act, May 2020
- $24.5 million loan from the EPA Water Infrastructure Finance and Innovation Act, April 2022
- $101 million loan from the State of California Clean Water State Revolving Fund
- $5.9 million sales and use tax exclusion from the California Alternative Energy and Advanced Transportation Financing Authority
Liquids Expansion Elements:
- Influent pump station expansion
- Headworks improvements
- Fine screen facility
- Two new primary clarifiers
- Existing aeration basin improvements
- New Membrane Bioreactor (MBR)
Solids Treatment Facility Elements:
- Rotary drum thickening building
- Digester facilities
- Centrifuge dewatering building
- Boiler building
- Digester gas treatment and flaring
- Food waste receiving
- Improvements to Existing Energy Recovery Engines